临床研究中病例与对照的选择:内附有趣例子
如何选择病例与对照
理想因果推断关系
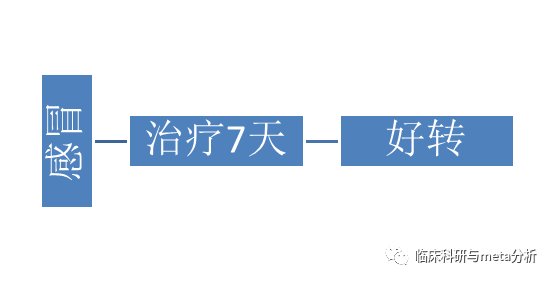
这个可以说治疗感冒有效吗?不能,因为感冒不治疗也可以在7天好转。
那么怎么办?就需要设立对照。
对照可以很好的决定研究结论的真实性;控制影响疗效的其他因素产生的混杂效应;消除安慰剂效应
对照分类
随机对照:对照与病例的纳入排除标准一致;对照与病例的纳入时间一样;对照与病例的纳入的干预是同期给与的;除了试验干预因素外,其他因素在两组分布尽量相同。根据对照组接受的干预措施,又可以分为空白对照,安慰剂对照,阳性对照
非随机对照:对照与病例的纳入排除标准一致;对照与病例的纳入时间一样;主要特点就是两组分配不是随机的,主要根据临床医师的决策。注意与观察性研究相区别。
另外还包括交叉对照以及历史对照。
通过脉冲点刺激治疗阻塞性呼吸睡眠障碍(OSAS)NEngl J Med 2014; 370:139-149
纳入标准:中重度的OSAS,且不能接受或坚持CPAP治疗的患者。
排除标准:Exclusion criteria were a body-mass index (BMI; the weight inkilograms divided by the square of the height in meters) of more than 32.0,neuromuscular disease, hypoglossal-nerve palsy, severe restrictive orobstructive pulmonary disease, moderate-to-severe pulmonary arterialhypertension, severe valvular heart disease, New York Heart Association classIII or IV heart failure, recent myocardial infarction or severe cardiacarrhythmias (within the past 6 months), persistent uncontrolled hypertensiondespite medication use, active psychiatric disease, and coexistingnonrespiratory sleep disorders that would confound functional sleep assessment.
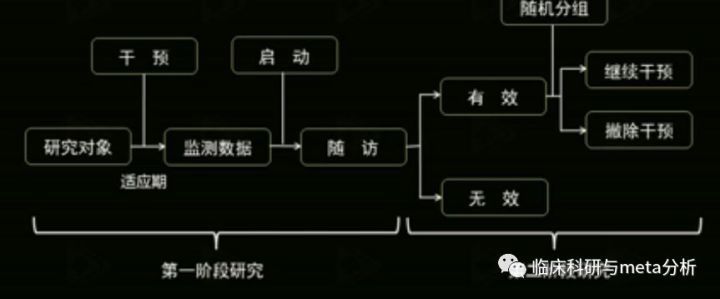
as a multicenter, prospective,single-group trial with participants serving as their owncontrols
多中心,前瞻性,单组病例非随机对照试验
At the 12-month visit, the first 46 consecutiveparticipants who met the criterion of having a response to therapy wererandomly assigned, in a 1:1 ratio, to the therapy-maintenance group or thetherapy-withdrawal group.
主要效果评估后跟随一个随机对照撤除试验
主要结局指标为:AHI 睡眠呼吸暂停指数
由下表可以看出干预期随访12个月,脉冲点刺激可以显著改善AHI。这个时候,就有问题,是脉冲点刺激起作用,还是疾病自然病程?接着看。
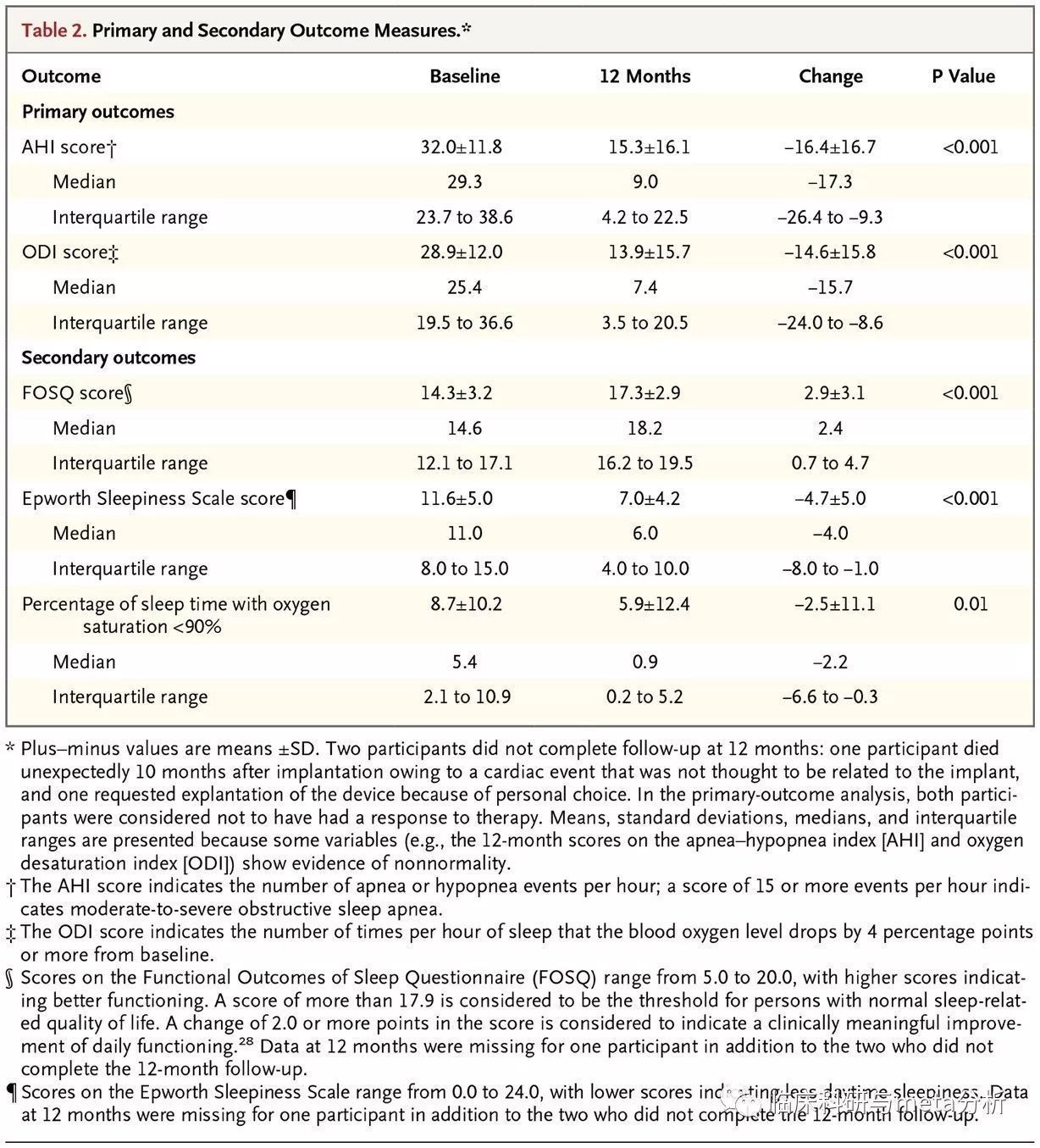
我们主要看下图中的上半部分,是指的主要研究指标,可以看到基线两组水平相似,干预随访12个月,效果都很好,然后将这些有效果的随机分组后,撤除治疗的AHI显著上升恶化,但是继续接受治疗的就保持了良好的效果。进一步证实了研究结果。